Occidental is Eyeing California’s Clean Fuels Market to Fund Texas Carbon Removal Plant
The oil company plans to remove carbon from the atmosphere and pump it into the ground to extract oil in the Permian Basin. Some climate activists fear the new technology is a cover for continuing to sell oil.
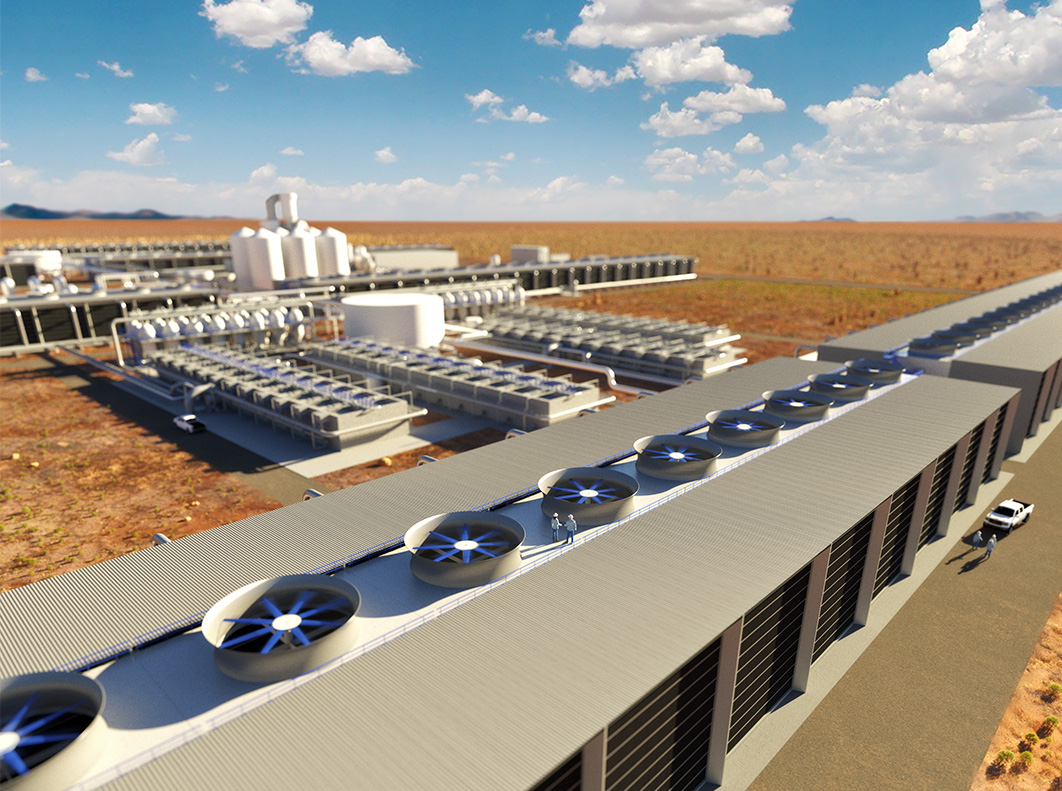
A rendering of a planned direct air capture plant in Texas that would initially pull 500,000 tons of carbon dioxide out of the air annually. Occidental Petroleum, which is planning to build the plant, would use some or most of the carbon dioxide it captures to pump more oil out of depleted reservoirs. Credit: Carbon Engineering
Occidental Petroleum is seeking to sell credits in California’s transportation carbon market to help finance the construction of what would be the world’s largest industrial carbon dioxide removal plant.
The operation would effectively invert what Occidental has done for a century, by taking carbon out of the air and sending it underground, even if on a relatively small scale.
But there’s a twist. Occidental has said it plans to use some or most of the carbon dioxide it captures from the Texas plant to squeeze more petroleum out of the ground, by pumping it into aging oil fields. As a result, the California carbon market, which is meant to help lower the climate emissions of transportation in the state, could supply tens of millions of dollars to help extract more oil, thereby contributing more emissions.
Occidental’s plans raise one of environmental advocates’ biggest concerns about carbon removal technologies: that they will be used by oil companies to delay the far more urgent task of rapidly transitioning away from fossil fuels. By allowing companies to sell credits for captured carbon dioxide used to produce oil, some advocates warn, California’s program is poised to do just that.
Data sources:





